The Palladian Style is a timeless architectural design. It originated in the 16th century in Italy.
This classic style, named after architect Andrea Palladio, has influenced buildings worldwide. Palladian architecture is known for its symmetry, proportion, and use of classical elements. This style often features columns, pediments, and a strong sense of balance. Palladio’s designs drew inspiration from the temples of ancient Rome and Greece.
Today, the Palladian style is admired for its elegance and simplicity. It remains popular in both residential and public buildings. Understanding the key features of Palladian architecture can help you appreciate its beauty and historical significance. In this blog, we explore the elements that define Palladian style and its impact on modern architecture.

Credit: www.homedit.com
Origins Of Palladian Style
The Palladian Style originated in the 16th century, inspired by the works of Italian architect Andrea Palladio. This style features symmetry, classical elements, and elegant proportions, reflecting the beauty of ancient Roman architecture.
The Palladian style is a revered architectural movement. It emerged during the Renaissance in Italy. This style boasts symmetry, proportion, and grandeur. Its origins are deeply rooted in the works of Andrea Palladio. His designs left a lasting mark on architecture.
Andrea Palladio’s Influence
Andrea Palladio was a renowned Italian architect. He lived in the 16th century. His work was deeply inspired by classical Roman architecture. Palladio’s designs emphasized harmony and balance. He authored “The Four Books of Architecture”. This book became a seminal text. It influenced architects across Europe and beyond. Palladio’s villas in Veneto are prime examples. They showcase his unique blend of classical and Renaissance elements.
Classical Inspirations
The Palladian style draws heavily from classical antiquity. Palladio admired the works of Vitruvius, an ancient Roman architect. He incorporated columns, pediments, and porticos into his designs. These elements evoke the grandeur of ancient Rome. Palladian buildings often feature a central hall. This hall is flanked by symmetrical wings. This design reflects the principles of classical architecture. Palladio’s use of mathematical ratios ensured perfect proportions. This attention to detail set his work apart. The Palladian style remains a symbol of elegance and sophistication.
Key Characteristics
The Palladian style is famous for its elegance and classical beauty. It draws inspiration from the architecture of ancient Rome and the works of Andrea Palladio. This section explores the key characteristics that define this timeless style.
Symmetry And Proportion
One of the most important features of the Palladian style is symmetry. Buildings are designed with a balanced and harmonious look. Each side of the structure mirrors the other, creating a sense of order and stability.
Proportion is another critical aspect. Palladian buildings follow precise mathematical ratios. These ratios ensure that every part of the building relates well to the whole. The result is a visually pleasing and well-balanced structure.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Symmetry | Each side of the building mirrors the other. |
| Proportion | Mathematical ratios ensure visual harmony. |
Columns And Porticos
Columns are a signature element of Palladian architecture. They are often tall and elegant, inspired by classical Greek and Roman designs. Columns can be found at the entrance or throughout the structure.
A portico is a porch with a roof supported by columns. It is usually found at the main entrance of the building. The portico adds grandeur and a classical touch to the structure.
- Columns provide structural support and aesthetic appeal.
- Porticos create a grand and welcoming entrance.
These elements work together to create buildings that are not only beautiful but also functional. The Palladian style remains popular due to its timeless appeal and classical roots.
Historical Significance
The Palladian Style holds a special place in architectural history. It emerged in the 16th century and has influenced many buildings. This style is known for its classical elements and symmetry. Let’s explore its historical significance in detail.
Renaissance Impact
The Palladian Style was born during the Renaissance. This period was marked by a revival of classical art and architecture. Andrea Palladio, an Italian architect, was the pioneer of this style. He admired Roman and Greek architecture. He used these influences to create buildings that were both functional and beautiful.
Palladio’s work included villas, churches, and palaces. His designs were guided by proportion, symmetry, and perspective. His famous book, “I Quattro Libri dell’Architettura,” spread his ideas across Europe. This book became a manual for many architects. They started to emulate his style in their own projects.
Adoption In Britain
The Palladian Style was enthusiastically adopted in Britain. This adoption began in the early 17th century. British architects were inspired by Palladio’s principles. They saw his style as a symbol of elegance and order.
One of the most notable adopters was Inigo Jones. He is often credited with introducing the Palladian style to England. Jones designed many famous buildings using Palladian principles. These include the Queen’s House in Greenwich and the Banqueting House in Whitehall.
Later, the style gained more popularity during the 18th century. Architects like Colen Campbell and Richard Boyle further promoted it. They designed several iconic buildings, including Chiswick House and Holkham Hall. These structures exemplify the symmetry and classical elements typical of the Palladian style.
The adoption of the Palladian style in Britain had a lasting impact. It influenced many public buildings, country houses, and even town planning. This style remains a testament to the enduring appeal of classical architecture.
Palladianism In The Modern Era
Palladianism, named after the Renaissance architect Andrea Palladio, is known for its symmetry and classical elements. This architectural style, rooted in 16th-century Italy, has influenced many buildings worldwide. Its principles are still visible today. Let’s explore how Palladianism has evolved and adapted in the modern era.
Revival In The 18th Century
The 18th century saw a significant revival of Palladian architecture. This period, often referred to as the Palladian Revival, brought back the style’s classical elegance. Architects in Britain and America embraced Palladian principles.
One notable example is the Chiswick House in London. Built in the 1720s, this villa exemplifies Palladian symmetry and proportion. Its design mirrors Palladio’s own works.
Another example is Thomas Jefferson’s Monticello in Virginia. Jefferson admired Palladio and incorporated his ideas into Monticello’s design. This house features a portico and classical columns, typical of Palladian architecture.
Contemporary Adaptations
Modern architects continue to draw inspiration from Palladian principles. They blend classical elements with contemporary designs. This fusion creates a timeless aesthetic.
For instance, some modern homes feature Palladian windows. These windows have a central arched section flanked by two rectangular sections. This design adds elegance and symmetry to contemporary buildings.
Commercial buildings also adopt Palladian features. The use of columns, pediments, and symmetry creates a sense of grandeur. This style is often seen in banks and government buildings.
Here is a table showcasing the key elements of Palladian architecture in contemporary designs:
| Element | Modern Use |
|---|---|
| Symmetry | Balance and harmony in layout |
| Columns | Support structures and decorative elements |
| Palladian windows | Elegant and iconic window designs |
| Pediments | Enhancing entrances and facades |
The timeless appeal of Palladian architecture ensures its continued relevance. Its principles of proportion, symmetry, and classical beauty resonate with both traditional and modern tastes.
Famous Palladian Structures
The Palladian style is famous for its classical beauty. Many structures show this style in different ways. These buildings are important in architecture history.
Villa Rotonda
Villa Rotonda is one of the most famous Palladian buildings. Architect Andrea Palladio designed it in the 16th century. It is located near Vicenza, Italy.
The villa has a unique design with a central dome. Each side of the building looks the same. This symmetry is a key feature of Palladian style. The villa is surrounded by beautiful gardens. Inside, the rooms have high ceilings and detailed decorations.
| Key Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Near Vicenza, Italy |
| Architect | Andrea Palladio |
| Design | Symmetrical with a central dome |
Chiswick House
Chiswick House is another famous Palladian structure. It is located in London, England. The house was built in the early 18th century by Lord Burlington.
The design of Chiswick House is inspired by Villa Rotonda. It has a central dome and symmetrical layout. The gardens around the house are also very beautiful.
- Location: London, England
- Built by: Lord Burlington
- Design: Inspired by Villa Rotonda
Chiswick House is a great example of Palladian style in England. It shows the influence of Italian architecture on English buildings.

Credit: architecturestyles.org
Influence On Modern Architects
The Palladian style, known for its symmetry and classical forms, has had a significant impact on modern architecture. Many architects have drawn inspiration from its principles, adapting them to contemporary designs. This section explores how Richard Boyle and Thomas Jefferson were influenced by Palladian ideals.
Richard Boyle’s Contributions
Richard Boyle, the 3rd Earl of Burlington, played a crucial role in popularizing the Palladian style in England. He was an architect and a great patron of the arts. Boyle admired the works of Andrea Palladio and aimed to bring the same elegance to British architecture.
Boyle’s designs, such as Chiswick House, showcase the key elements of Palladian architecture. These include:
- Symmetrical facades
- Classical columns
- Proportional design
He also collected and published Palladio’s works, making them accessible to other architects. This contributed significantly to the style’s spread across Europe.
Thomas Jefferson’s Designs
Thomas Jefferson, the third President of the United States, was also an architect. He was deeply influenced by Palladian principles. Jefferson believed that architecture should reflect the ideals of democracy and classical beauty.
Jefferson’s most famous work, Monticello, embodies the Palladian style. It features:
- A central dome
- Symmetrical layout
- Use of classical orders
He also designed the Virginia State Capitol based on Palladian principles. Jefferson’s designs have left a lasting legacy on American architecture, blending classical beauty with functional design.
Palladian Interiors
The Palladian style brings a sense of grandeur and elegance. Its interiors are known for their symmetry, balance, and use of classical elements. Let’s explore the key features that define Palladian interiors.
Elegant Interiors
Palladian interiors often feature high ceilings and large windows. These elements create bright and airy spaces. Symmetry is a core principle in Palladian design. Rooms are arranged to mirror each other, creating a balanced and harmonious look.
Columns and arches are common. They add a touch of classical beauty. The use of natural materials like marble and wood enhances the elegance of the interiors. Floors often have intricate patterns, adding a layer of sophistication.
Furniture And Décor
Furniture in Palladian interiors is both functional and decorative. Pieces are often made from high-quality materials like mahogany and walnut. Upholstery is usually in muted colors and luxurious fabrics like silk and velvet.
Décor items often include antique vases, mirrors, and chandeliers. These items add a touch of timeless beauty. Artwork plays a significant role as well. Portraits, landscapes, and classical scenes adorn the walls.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Symmetry | Rooms mirror each other for balance |
| Columns and Arches | Classical elements adding beauty |
| Natural Materials | Marble and wood for elegance |
| High-quality Furniture | Mahogany and walnut pieces |
| Luxurious Fabrics | Silk and velvet upholstery |
| Antique Décor | Vases, mirrors, and chandeliers |
| Artworks | Portraits and landscapes |
Palladian interiors create a serene and elegant atmosphere. The use of classical elements and high-quality materials ensures a timeless appeal.
Sustainability And Palladian Principles
The Palladian style, inspired by the architect Andrea Palladio, emphasizes balance, symmetry, and proportion. While it originates from the 16th century, its principles can adapt to modern sustainability needs. Let’s explore how the Palladian style aligns with eco-friendly and energy-efficient practices.
Eco-friendly Adaptations
Modern architects reinterpret Palladian designs with eco-friendly materials. For instance, they use locally-sourced stone and timber, reducing transportation emissions.
Additionally, many Palladian buildings now incorporate green roofs. These roofs support plant life, improve insulation, and manage rainwater.
| Palladian Principle | Eco-friendly Adaptation |
|---|---|
| Symmetry | Balanced window placements for natural light |
| Proportion | Use of renewable materials in correct ratios |
| Harmony | Integration with natural surroundings |
Energy Efficiency
The Palladian style naturally supports energy efficiency. Large windows and high ceilings allow for excellent ventilation.
Furthermore, the symmetry in design helps with optimal placement of solar panels. This ensures maximum sunlight exposure throughout the day.
Many Palladian buildings also feature thick walls, which provide superior insulation. This reduces the need for artificial heating and cooling.
- Large windows for natural light
- High ceilings for better air circulation
- Thick walls for improved insulation
- Strategic placement of solar panels
By combining these traditional principles with modern technology, the Palladian style offers a blend of elegance and sustainability. It stands as a timeless example of how historical designs can meet contemporary needs.
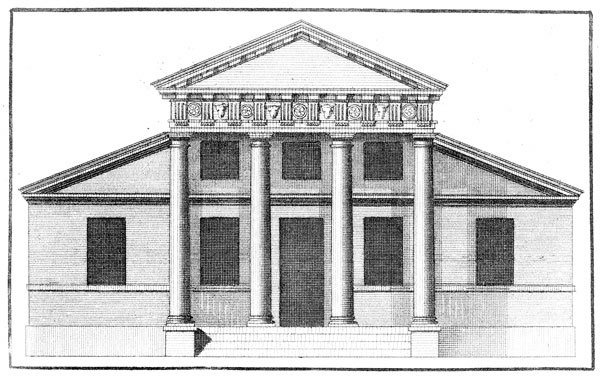
Credit: en.wikipedia.org
FAQs
What Is Palladian Style Architecture?
Palladian style architecture is a European architectural style inspired by the designs of Venetian architect Andrea Palladio. It emphasizes symmetry, classical forms, and grandeur.
When Did The Palladian Style Emerge?
The Palladian style emerged in the 16th century during the Italian Renaissance. It gained popularity in Britain and other European countries in the 17th and 18th centuries.
What Are Key Features Of Palladian Style?
Key features of Palladian style include symmetry, classical elements like columns and pediments, and use of proportional design. It often incorporates grand facades and elegant details.
Why Is Palladian Style Popular?
Palladian style is popular for its timeless elegance, balanced proportions, and classical beauty. It represents sophistication and historical grandeur.
Conclusion
The Palladian Style offers timeless elegance and simplicity. Its symmetry and classical elements create beauty in architecture. This style blends both function and form effortlessly. It remains popular for its versatility and aesthetic appeal. Whether in homes or public buildings, Palladian design stands out.
Explore this style for your next architectural project. Its charm is truly enduring and captivating. Embrace the Palladian Style and add a touch of history to your space.







