Methodism is a Christian denomination with millions of followers worldwide. It has a rich history and unique beliefs that distinguish it from other denominations.
Originating in the 18th century, Methodism began as a movement within the Church of England. It was founded by John Wesley and his brother Charles. They emphasized a methodical approach to faith, hence the name “Methodism. ” This denomination focuses on personal faith, social justice, and community service.
Followers believe in a life of piety and good works. Methodism has contributed significantly to education, health, and social reforms. Understanding its principles and history can offer deeper insights into its impact and relevance today. Join us as we explore the core elements of Methodism and its enduring legacy.

Credit: goodnewsmag.org
Origins Of Methodism
Methodism began in the 18th century. It originated as a revival movement within the Church of England. The movement focused on personal faith, social justice, and community. Methodism quickly spread across Britain and beyond.
Early Influences
The early influences of Methodism can be traced back to the religious climate of the 18th century. This period saw a desire for spiritual renewal. Many people felt disconnected from the formal and rigid practices of the Church of England.
Several religious groups influenced Methodism. These included the Moravians and the Puritans. Their emphasis on personal piety and communal worship resonated with many.
Founders And Key Figures
John Wesley is widely regarded as the founder of Methodism. Born in 1703, he was a clergyman in the Church of England. Wesley, along with his brother Charles, began organizing small groups for prayer and Bible study.
Another key figure was George Whitefield. A dynamic preacher, Whitefield played a significant role in spreading the Methodist message. His powerful sermons attracted large crowds and inspired many to join the movement.
Charles Wesley contributed significantly through his hymns. His songs helped shape the identity of Methodism. They remain a central part of Methodist worship today.
| Key Figure | Contribution |
|---|---|
| John Wesley | Founder, organized small groups |
| Charles Wesley | Hymn writer |
| George Whitefield | Preacher, spread Methodist message |
The efforts of these founders laid the groundwork for the growth of Methodism. Their legacy continues to influence the denomination today.
Core Beliefs
Methodism is a denomination within Christianity. It emphasizes faith, love, and service. These core beliefs shape the lives of Methodists around the world.
Doctrine And Theology
Methodists believe in the Trinity. This means they believe in God the Father, Jesus Christ the Son, and the Holy Spirit.
They follow the teachings of John Wesley, who stressed personal faith and social justice. Methodists believe in salvation through faith in Jesus Christ. They also believe in the importance of good works. This means helping others and acting with love and kindness.
Methodists also emphasize the importance of grace. They believe that God’s grace is available to all people. This grace helps them grow in their faith and become better people.
Practices And Rituals
Methodists have several important practices and rituals. These include worship services, prayer, and the sacraments.
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Worship Services | Held on Sundays, these services include singing, prayers, and a sermon. |
| Prayer | Prayer is central to Methodist life. They pray individually and in groups. |
| Sacraments | Methodists observe two sacraments: Baptism and Holy Communion. |
Baptism is a ritual of initiation. It welcomes new members into the church. Holy Communion is a ritual that remembers the Last Supper of Jesus Christ. It is a time for reflection and renewal of faith.
Methodists also believe in social action. They work to improve their communities. They help the poor, the sick, and the oppressed. This is part of their commitment to living out their faith.
Historical Development
Methodism is a major Protestant Christian tradition. Its roots trace back to the 18th century. This movement has a rich and diverse history. The historical development of Methodism involves its expansion in Britain and growth in America.
Expansion In Britain
Methodism began in Britain in the 18th century. John Wesley and his brother Charles Wesley were its founders. They started as a revival movement within the Church of England. They aimed to bring more people to Christ. Their strong preaching attracted many followers.
John Wesley traveled extensively across Britain. He preached in open fields, reaching the common folk. This approach helped Methodism spread quickly. The movement emphasized personal faith, social justice, and charity. This resonated with many people.
Small groups or “classes” formed for study and prayer. These groups met regularly. They fostered a sense of community and support. Over time, Methodism grew beyond the Church of England. It became a separate denomination. By the end of the 18th century, Methodism had many followers across Britain.
Growth In America
Methodism crossed the Atlantic to America in the late 18th century. Early Methodists were active in spreading the faith. Francis Asbury was a key figure in American Methodism. He traveled thousands of miles on horseback, preaching and organizing new congregations.
Methodism grew rapidly in the American frontier. Its simple and direct message appealed to many. The church structure allowed laypeople to take on leadership roles. This was attractive in the democratic spirit of the new nation.
The Methodist Church played a significant role in American society. It promoted education, temperance, and abolition of slavery. By the mid-19th century, Methodism became one of the largest denominations in the United States. Its influence continues to this day.
Methodism And Social Reform
Methodism has a rich history of advocating for social change. The movement has been instrumental in addressing various social issues. Methodists have played significant roles in improving society through various initiatives.
Abolition Of Slavery
The Methodist Church was a strong advocate for the abolition of slavery. Many Methodists believed that slavery was morally wrong. They actively campaigned against it. Leaders like John Wesley and William Wilberforce were vocal opponents of slavery.
Methodists organized meetings and wrote pamphlets to raise awareness. They also collaborated with other abolitionists. Their efforts significantly contributed to the abolition movement in both the United States and the United Kingdom.
Educational Initiatives
Methodists have always valued education. They believed it was essential for personal and societal development. Methodists established numerous schools and educational programs. These initiatives aimed to provide education to all, regardless of social status.
Many Methodist schools focused on teaching basic literacy. They also emphasized moral and religious education. This approach helped shape many young minds and contributed to social progress.
Below is a table highlighting some key educational initiatives by Methodists:
| Initiative | Year Established | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Sunday Schools | 1780 | Basic literacy and religious education |
| Methodist Colleges | 19th Century | Higher education and professional training |
| Community Outreach Programs | 20th Century | Adult education and vocational training |
These initiatives have left a lasting impact on society. Methodists continue to support and promote educational opportunities for all.
Modern Methodism
Modern Methodism has evolved significantly while retaining its core principles. This branch of Christianity is grounded in the teachings of John Wesley. Today, it faces contemporary issues and boasts a global presence.
Contemporary Issues
Modern Methodism grapples with various social and ethical issues. Topics like gender equality and LGBTQ+ rights are at the forefront. Many Methodists seek to balance tradition with progressive values. They strive to create inclusive communities. This includes diverse voices within their congregations.
Climate change is another critical issue. Methodist churches advocate for environmental stewardship. They encourage sustainable practices within their communities. Health care access also remains a priority. Methodists support initiatives to provide care for the underserved.
Global Presence
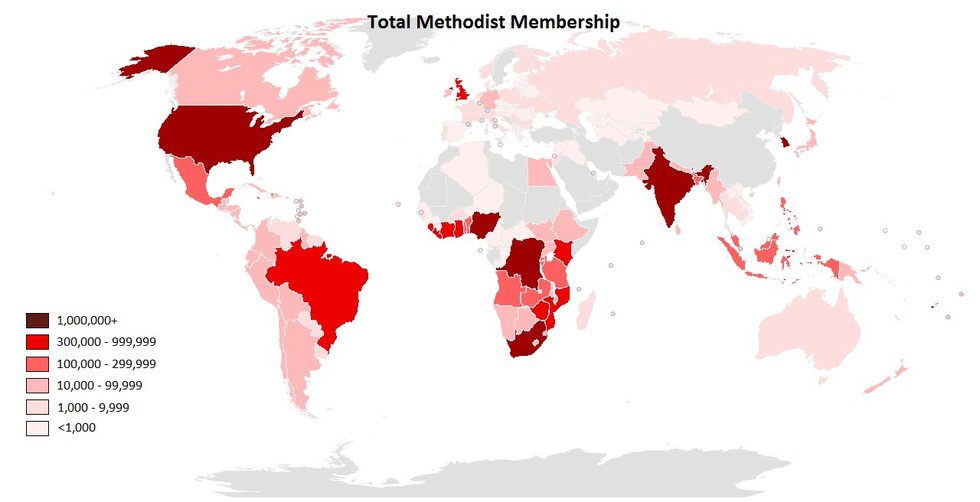
Methodism has a strong global presence. It spans continents and cultures. Africa, Asia, and Latin America have growing Methodist communities. Each region brings its unique perspective. This diversity enriches the global Methodist family.
The United Methodist Church is one of the largest bodies. It has millions of members worldwide. Mission work remains central to its identity. Methodists engage in humanitarian efforts. They provide education, health care, and disaster relief. These initiatives reflect their commitment to social justice.
Modern Methodism continues to adapt and grow. It faces new challenges with resilience. Its global presence and commitment to inclusivity drive its evolution.
Worship And Community Life
Methodism is not just a religion. It’s a way of life. Worship and community life are central to Methodism. Church services bring people together to praise God. Community outreach helps those in need. This balance strengthens faith and bonds within the community.
Church Services
Methodist church services are rich in tradition. They often include hymns, prayers, and a sermon. Services are a time for reflection. They help members grow spiritually. Many churches hold services on Sunday mornings. Some also have evening services.
Services are open to everyone. Visitors are always welcome. The atmosphere is warm and inclusive. This helps newcomers feel at ease. Services usually last about an hour. Some may be longer on special occasions.
Communion is a key part of worship. It is celebrated regularly. All are invited to take part. This symbolizes unity in the faith.
Community Outreach
Methodists believe in helping others. Community outreach is a big part of their mission. This includes food drives, clothing donations, and more. Volunteers often visit the sick and elderly. They offer comfort and support.
Many churches have programs for children and youth. These programs teach values and life skills. They also provide a safe space for kids to grow.
Outreach efforts go beyond the local community. Many Methodists support global missions. These missions provide aid to those in need around the world. This could be in the form of medical help, education, or disaster relief.
Being active in the community strengthens bonds. It also reflects the teachings of Jesus. Helping others is a way to live out one’s faith. This makes Methodism a very hands-on religion.
Notable Methodist Leaders
Methodism has a rich history filled with influential leaders who have shaped its doctrine and practice. These leaders, both past and present, have contributed significantly to the growth and development of the Methodist movement. Their dedication and vision continue to inspire millions around the world.
Historical Figures
John Wesley, the founder of Methodism, is the most notable historical figure. His teachings and sermons laid the foundation for the Methodist Church. Charles Wesley, his brother, wrote many hymns that are still sung today. Another important leader was Francis Asbury, who played a key role in spreading Methodism in America.
George Whitefield, a contemporary of the Wesleys, also influenced the early Methodist movement. His powerful preaching attracted large crowds and helped expand Methodism’s reach. Thomas Coke, known as the father of Methodist missions, established many Methodist societies worldwide.
Current Leaders
Bishop Cynthia Fierro Harvey, the President of the Council of Bishops, is a prominent leader in the United Methodist Church. Her leadership focuses on social justice and community outreach. Bishop William T. McAlilly, another influential leader, oversees the Nashville Episcopal Area.
Rev. Dr. J. Kabamba Kiboko, the first African woman bishop in the United Methodist Church, has made significant contributions. Her work in promoting gender equality and education is widely recognized. These leaders, among others, continue to guide the Methodist Church in its mission and outreach.
Credit: um-insight.net
Impact On Christianity
The impact of Methodism on Christianity has been profound. Methodism has influenced various aspects of the Christian faith. Its teachings and practices have shaped many denominations and fostered unity among Christians.
Ecumenical Relations
Methodism has played a key role in promoting ecumenical relations. It has encouraged dialogue between different Christian denominations. Methodists have often sought to bridge gaps between diverse Christian traditions. This focus on unity has led to many collaborative efforts. These efforts include joint worship services and shared community projects.
Influence On Other Denominations
Methodism’s influence extends to many Christian denominations. It has inspired various aspects of worship and governance. For example, the Methodist emphasis on personal holiness has resonated with other faith communities. This has led to the adoption of similar practices in other denominations.
Moreover, the Methodist practice of small group meetings has been widely adopted. These meetings, often called class meetings, promote spiritual growth and accountability. Other denominations have incorporated this practice to enhance their own spiritual communities.
Methodism has also contributed to social justice movements. Its strong commitment to social issues has inspired other Christians. Many denominations now engage in social justice efforts, influenced by the Methodist tradition.
| Aspect | Influence |
|---|---|
| Personal Holiness | Adopted by other denominations |
| Class Meetings | Incorporated into spiritual practices |
| Social Justice | Inspired social justice movements |
FAQs
What Is Methodism?
Methodism is a Protestant Christian movement founded by John Wesley. It emphasizes personal faith, social justice, and communal worship. Methodists follow the teachings of Jesus Christ and the Bible.
Who Founded Methodism?
John Wesley, an Anglican cleric, founded Methodism in the 18th century. He emphasized personal faith and social activism. His leadership inspired a global movement.
What Do Methodists Believe?
Methodists believe in salvation through faith in Jesus Christ. They emphasize personal holiness, social justice, and community service. The Bible is their central religious text.
How Is Methodist Worship Unique?
Methodist worship combines liturgical practices with contemporary elements. Services include hymns, prayers, sermons, and sacraments. They focus on personal and communal relationship with God.
Conclusion
Methodism offers a unique approach to faith and community. Its history is rich and inspiring. Many find comfort and guidance in its teachings. Methodism emphasizes love, service, and personal growth. It encourages a strong sense of community. This faith tradition continues to grow worldwide.
Exploring Methodism can deepen your spiritual journey. Discover its values and see how they resonate with you. Embrace the opportunity to learn and grow. Methodism might be the path you seek.