The Good Friday Agreement in 1998 marked a turning point for peace. It brought hope to Northern Ireland after years of conflict.
This historic accord ended decades of violence known as “The Troubles. ” It was a time when communities were divided by political and religious differences. The agreement was a result of long negotiations. Leaders from different groups came together. They aimed for peace and a better future for all.
This moment in history showed the power of dialogue and compromise. It paved the way for a more peaceful Northern Ireland. Understanding this agreement helps us see how peace can be achieved. It offers lessons for resolving conflicts around the world. Let’s explore the significance and impact of the Good Friday Agreement.

Credit: www.ejiltalk.org
Historical Context
The Good Friday Agreement of 1998 marked a pivotal moment in history. It ended decades of conflict in Northern Ireland. Understanding the historical context is crucial to grasp its significance. This context includes deep-rooted tensions and previous peace efforts.
Tensions In Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland experienced significant tensions in the 20th century. This period was marked by a conflict known as “The Troubles.” Violence and unrest defined everyday life for many. The conflict stemmed from political and religious differences. Catholics wanted unification with Ireland. Protestants preferred to remain part of the United Kingdom. These differing aspirations led to prolonged conflict and division.
Previous Peace Efforts
Efforts to establish peace in Northern Ireland occurred before 1998. The Sunningdale Agreement of 1973 was one such attempt. It aimed to create a power-sharing executive. Yet, it collapsed due to lack of support. Another effort was the Anglo-Irish Agreement in 1985. This agreement sought cooperation between the British and Irish governments. Despite these efforts, lasting peace remained elusive. The persistent search for peace set the stage for the Good Friday Agreement.
Key Figures
The Good Friday Agreement in 1998 marked a pivotal moment in Irish history. It ended years of conflict in Northern Ireland. Key figures played crucial roles in achieving this peace. Their leadership and vision brought about significant change. Understanding these figures helps us appreciate this historic accord.
Political Leaders
Several political leaders were instrumental in the Good Friday Agreement. Tony Blair, the British Prime Minister, showed unwavering commitment. He worked tirelessly to bring parties together. Bertie Ahern, the Irish Taoiseach, provided strong support from the Republic of Ireland. His collaboration with Blair was vital. John Hume, leader of the Social Democratic and Labour Party, pushed for peaceful solutions. His efforts earned him the Nobel Peace Prize. David Trimble, leader of the Ulster Unionist Party, took bold steps towards peace. His leadership was crucial for unionist support.
International Influences
International figures also influenced the peace process. U.S. President Bill Clinton played a significant role. His administration encouraged dialogue and provided diplomatic support. Senator George Mitchell acted as a key mediator. His patience and neutrality were essential in negotiations. The European Union supported the peace process. Their involvement provided economic and political backing. These international contributions were vital. They helped ensure a lasting peace in Northern Ireland.
The Agreement Details
The Good Friday Agreement, signed in 1998, marked a new era for Northern Ireland. It aimed to end decades of conflict known as “The Troubles.” This agreement brought hope for peace and prosperity. Let’s delve into the key details of this historic accord.
Main Provisions
The Good Friday Agreement outlined several important provisions. It confirmed Northern Ireland’s status as part of the UK. This status would change only if the majority wished so. It also recognized the right of people to identify as British, Irish, or both.
Another key provision was the decommissioning of weapons. This aimed to disarm all paramilitary groups. The agreement also emphasized human rights and equality for all citizens. It promised reforms in policing and justice systems.
Power-sharing Arrangements
The agreement introduced a power-sharing government. This system ensured representation from both unionist and nationalist parties. The Northern Ireland Assembly was established for local governance. It consisted of 108 elected members.
Key decisions required cross-community support. This meant both communities had to agree. The power-sharing executive included ministers from major parties. This arrangement promoted cooperation and mutual respect.
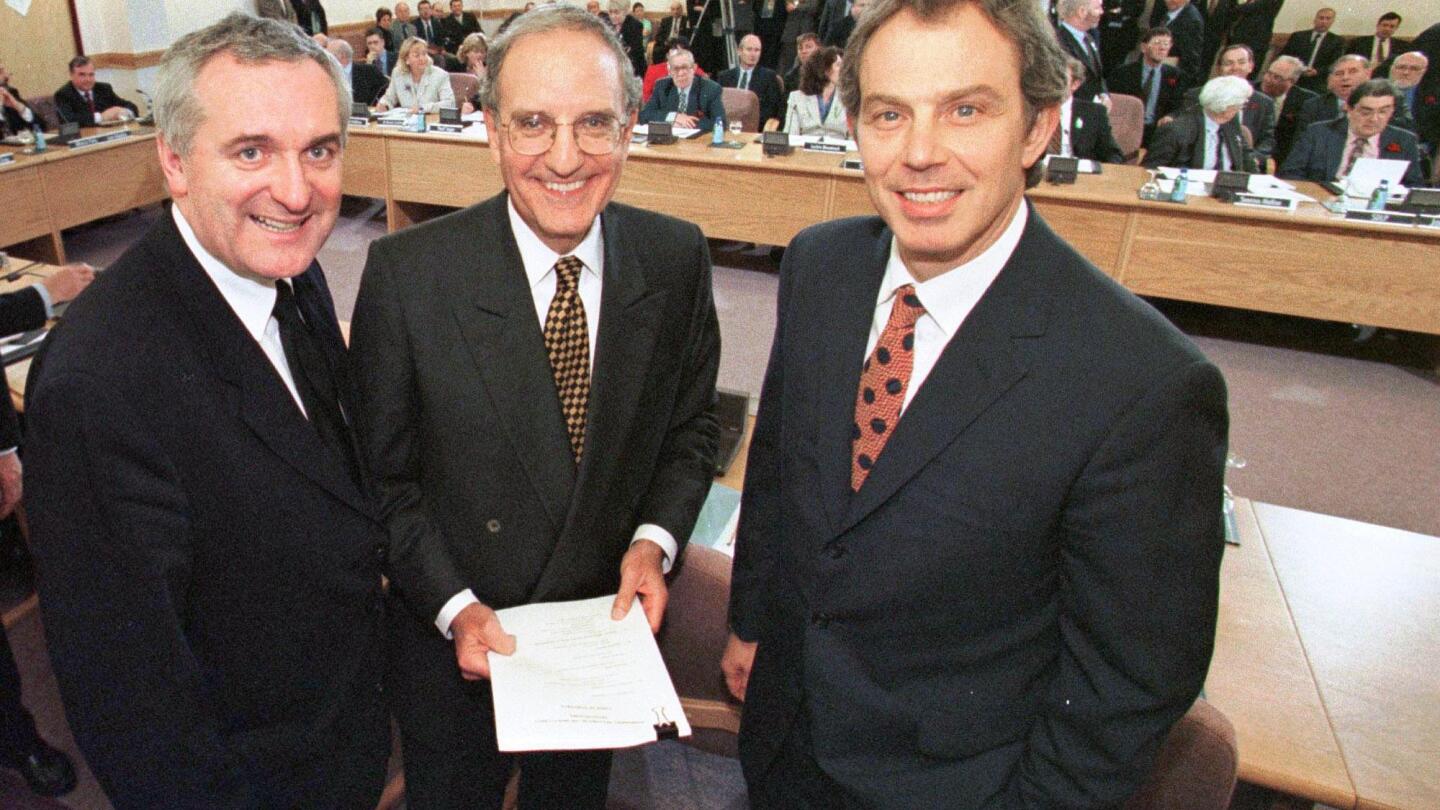

Credit: apnews.com
Impact On Northern Ireland
The Good Friday Agreement in 1998 changed Northern Ireland. It ended years of conflict and brought peace. People now live with less fear and more hope for the future.
The Good Friday Agreement of 1998 marked a monumental shift in Northern Ireland’s landscape. Its effects rippled through communities, bringing profound changes. As you navigate through its impact, you’ll uncover stories of transformation, growth, and new possibilities that emerged from this pivotal moment in history.
Reduction In Violence
One of the most significant impacts of the Good Friday Agreement was the reduction in violence. Before 1998, Northern Ireland was plagued by conflict and unrest. The streets often echoed with tension, affecting everyday life.
Post-agreement, peace took root. Families began to feel safer, and children could play outside without fear. This change was palpable. Can you imagine the relief of waking up to a quieter, safer neighborhood? The agreement turned that dream into reality, providing a fresh start for many.
Economic Growth
Peace brought economic opportunities. With stability, businesses started to flourish. Investors felt confident, leading to increased job creation and economic development.
Picture this: bustling shops and cafes, lively markets, and growing industries. Northern Ireland’s economy began to thrive. As you walk through cities like Belfast today, the vibrant economy is hard to miss. The agreement opened doors to prosperity, allowing people to envision brighter futures.
In essence, the Good Friday Agreement reshaped Northern Ireland’s future. As you reflect on its impact, consider how peace and economic growth transformed lives. What possibilities can emerge when communities embrace peace and progress?
Challenges Post-agreement
The Good Friday Agreement in 1998 was a milestone in peace efforts. Yet, significant challenges emerged post-agreement. The journey to lasting peace faced obstacles. These obstacles highlighted the complexities of Northern Ireland’s past. Let’s explore these challenges further.
Sectarian Divides
Sectarian divides remained a deep-rooted issue post-agreement. Communities still lived in separate areas. Schools often segregated by religion. These divides fueled mistrust and fear. Many found it hard to reconcile past grievances. Events like parades sometimes reignited old tensions. The peace walls, meant to protect, symbolized division. Overcoming these divides required patience and dialogue.
Political Struggles
Political struggles also tested the agreement’s strength. Power-sharing demanded cooperation from opposing parties. Yet, mistrust slowed progress. Political disagreements often stalled government functions. The lack of trust stemmed from years of conflict. Leaders needed to build bridges and find consensus. Political stability was crucial for lasting peace. Many struggled to find common ground for governance.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Role Of The United States
The United States played a key role in the Good Friday Agreement in 1998. By mediating talks, it helped Northern Ireland move towards peace. U. S. involvement was crucial in bridging divides and fostering trust among parties.
The Good Friday Agreement of 1998 marked a pivotal moment in the history of Northern Ireland, bringing an end to decades of conflict known as “The Troubles.” While the agreement was primarily a local effort, the role of the United States was crucial in facilitating the peace process. The diplomatic maneuvers and the influence of American leadership helped pave the way for the historic accord. How did the United States contribute to this monumental peace agreement? Let’s delve into its diplomatic interventions and presidential influence.
Diplomatic Interventions
The United States played a key diplomatic role in the Good Friday Agreement through its special envoy, Senator George Mitchell. His tireless mediation efforts were instrumental in bringing conflicting parties to the negotiation table.
Mitchell’s approach was simple yet effective—listening patiently and ensuring all voices were heard. His insistence on deadlines and structured talks kept the discussions focused.
The U.S. also provided a neutral ground for dialogue, helping to ease deep-seated tensions. This diplomatic support was vital in creating a conducive environment for peace.
Presidential Influence
President Bill Clinton’s involvement in the peace process was significant. By visiting Northern Ireland, he underscored the commitment of the United States to support the peace effort.
Clinton’s speeches emphasized hope and reconciliation, resonating with people on both sides of the conflict. His administration was proactive in encouraging dialogue and compromise.
The president’s personal engagement demonstrated that international leaders could indeed play a positive role in resolving local disputes. What can you learn from Clinton’s approach to leadership in complex situations?
In reflecting on the U.S. role in the Good Friday Agreement, it’s clear that diplomatic strategies and presidential influence can profoundly impact peace processes. While the agreement was a collective achievement, the support of the United States was undeniably a cornerstone of its success. As you ponder these insights, consider how similar strategies might be employed in current global conflicts. What role can you play in fostering peace in your community?
Commemoration And Legacy
The Good Friday Agreement in 1998 marked a turning point in history. Its impact continues to resonate, shaping the political landscape of Northern Ireland. Commemorating this crucial event involves recognizing its legacy and influence on society.
Annual Celebrations
Every year, the Good Friday Agreement is honored with ceremonies. These events bring communities together to reflect on peace and progress. Officials and citizens gather to discuss the strides made since 1998. Parades and cultural activities highlight shared values and cooperation. Participants celebrate the spirit of reconciliation and unity. These celebrations serve as a reminder of the importance of dialogue.
Educational Programs
Schools and institutions play a key role in commemorating the agreement. Educational programs focus on teaching the history and significance of 1998. Students learn about conflict resolution and peace-building. Workshops encourage critical thinking and empathy among young learners. These programs aim to foster an understanding of past struggles. By educating youth, society builds a future grounded in peace.
Lessons For Global Peace
The Good Friday Agreement in 1998 taught valuable lessons for global peace. It showed the power of dialogue in resolving conflicts. By fostering cooperation and understanding, this historic accord brought lasting peace to Northern Ireland.
The Good Friday Agreement of 1998 stands as a landmark event in the journey toward peace in Northern Ireland. Its success offers valuable insights for achieving global peace. The agreement’s innovative strategies can guide you in resolving conflicts and fostering international cooperation. By examining these lessons, you can better understand how peace can be achieved in other troubled regions around the world.
Conflict Resolution Strategies
The Good Friday Agreement introduced several effective conflict resolution strategies. It recognized the importance of dialogue among conflicting parties. Open discussions allowed for the airing of grievances and the building of trust. You can apply this by encouraging open communication in disputes, whether they’re personal or global.
The agreement also emphasized the importance of compromise. It required parties to make concessions for the greater good. Consider how compromise can resolve disagreements in your life or community. Are you willing to give a little to gain a lot? This mindset was crucial in transforming the conflict in Northern Ireland into a peaceful society.
International Cooperation
International cooperation played a key role in the success of the Good Friday Agreement. The involvement of external parties like the United States and the European Union provided crucial support. Their participation helped mediate the talks and ensure fair outcomes. This highlights the importance of seeking external help when solving complex problems.
Think about how international partnerships can aid in conflict resolution. Countries often have unique perspectives and resources that can contribute to peace. You might ask yourself: How can global cooperation help tackle issues in your community or country? The Good Friday Agreement shows the power of working together beyond borders.
By learning from the Good Friday Agreement, you can explore how these strategies apply to different conflicts. The lessons of dialogue, compromise, and international cooperation aren’t just historical—they’re tools for today and tomorrow. In what ways will you use these lessons to foster peace in your world?
FAQs
What Did The 1998 Good Friday Agreement Do?
The 1998 Good Friday Agreement established peace in Northern Ireland. It created a power-sharing government. The agreement recognized both British and Irish identities. It addressed issues like decommissioning weapons and prisoner releases. This historic pact ended decades of conflict known as “The Troubles”.
What Happened Between Ireland And England In The 90s?
Ireland and England experienced significant political tensions in the 1990s. The Northern Ireland peace process aimed to resolve conflicts between nationalist and unionist communities. The Good Friday Agreement in 1998 marked a major milestone, establishing a framework for peace and cooperation between the two nations.
What Was The Turnout Of The Good Friday Agreement Referendum In 1998?
The Good Friday Agreement referendum in 1998 had a voter turnout of 81. 1% in Northern Ireland. This significant participation highlighted the public’s engagement in the peace process. The agreement aimed to bring peace and stability to the region after decades of conflict.
What Ended The Troubles In Ireland?
The Troubles in Ireland ended with the Good Friday Agreement in 1998. It established a power-sharing government. This peace accord involved multiple political parties and governments. The agreement aimed to address issues, reduce violence, and promote cooperation. Its success hinged on mutual commitment to peace and reconciliation.
Conclusion
The Good Friday Agreement marked a new era for peace. It brought hope to divided communities in Northern Ireland. Leaders and citizens worked together for a better future. Trust and dialogue paved the way for lasting change. The agreement showed the power of cooperation.
It taught valuable lessons about unity and understanding. Today, its legacy continues to inspire efforts for peace worldwide. The journey wasn’t easy, but the results were profound. The Good Friday Agreement remains a symbol of hope and possibility. It reminds us that peace is achievable when people unite for a common goal.