The Falklands War was a brief but intense conflict in 1982. It involved Argentina and the United Kingdom fighting over the Falkland Islands.
This war, lasting just over two months, drew global attention due to its unexpected nature and the strategic significance of the islands. The Falklands, remote yet valuable, became the center of a military confrontation that tested the political resolve and military capabilities of both nations.
It highlighted issues of sovereignty, national pride, and international diplomacy. Understanding this war offers insights into geopolitical strategies and the complexities of territorial disputes. This introduction sets the stage for exploring the events, causes, and outcomes of the Falklands War, revealing its impact on world history and relations.
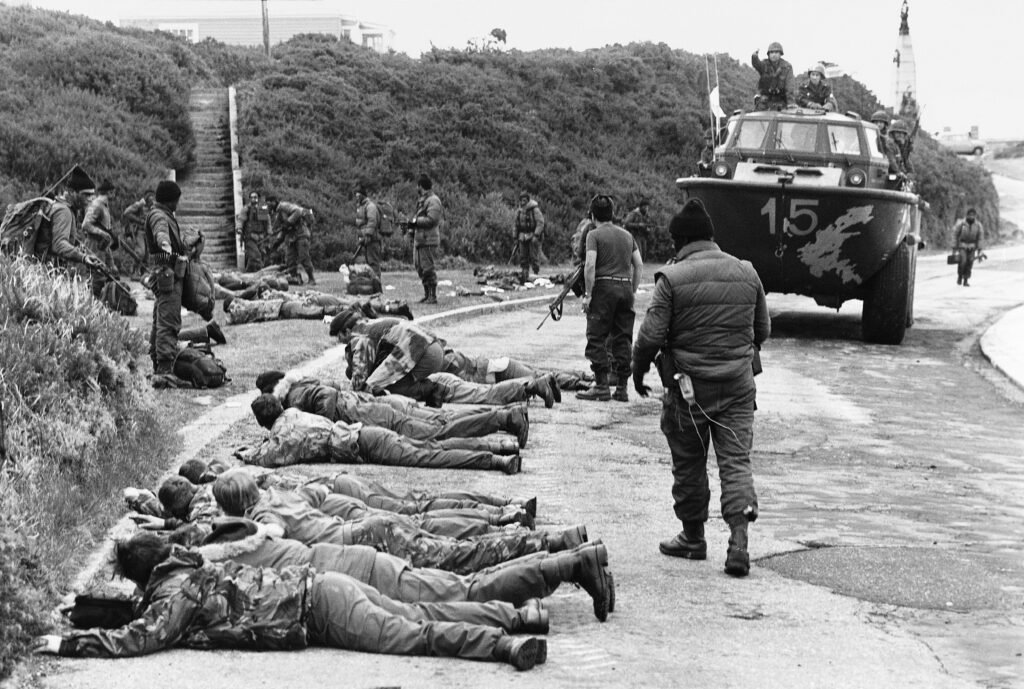

Credit: www.historyextra.com
Origins Of The Conflict
The Falklands War began with Argentina’s invasion of the islands in April 1982. Britain claimed sovereignty, leading to a military conflict. Historical disputes over ownership fueled tensions between the two nations.
The Falklands War is a pivotal event in modern history, rooted in a complex web of historical claims and political tensions. Understanding the origins of this conflict helps us grasp why nations go to war over seemingly small territories.
Can a piece of land really hold such power?
Understanding the beginnings of the Falklands War is like piecing together a historical puzzle, where each piece reveals a story of sovereignty, politics, and national pride.
Historical Background
The Falkland Islands have been the subject of territorial disputes for centuries. Various countries, including France, Spain, and Britain, have laid claim to the islands since the 18th century.
By 1833, Britain had established its control over the Falklands, a fact that Argentina has contested ever since. This simmering dispute was fueled by national pride on both sides.
The islands, located in the South Atlantic, are just 300 miles off the coast of Argentina. This proximity intensified Argentina’s belief that the islands rightfully belonged to them.
Political Tensions
Political tensions between Argentina and Britain escalated in the late 20th century. In the years leading up to the war, Argentina was under a military dictatorship, which was desperate to rally public support.
Claiming the Falklands was seen as a way to unite the country and distract from domestic issues. Meanwhile, Britain’s political landscape was also fraught with challenges, including economic struggles and declining global influence.
In early 1982, Argentina landed troops on the islands, expecting a swift victory. The military junta in Argentina underestimated Britain’s resolve and the international implications of such a bold move.
Did the leaders fully grasp the cost of conflict?
These tensions set the stage for a war that would last ten weeks, testing the resolve of both nations and leaving a lasting impact on their people. Understanding these origins helps us see how fragile peace can be when national pride and politics collide.
By learning from history, can we prevent such conflicts in the future?
Key Players And Leaders
During the Falklands War, key figures shaped its course. Margaret Thatcher led Britain with firm resolve, while Leopoldo Galtieri’s decisions influenced Argentina’s strategy. Their leadership left lasting impacts on international relations.
The Falklands War, though brief, was marked by significant leadership from both the British and Argentine sides. Understanding the key players and leaders involved offers insights into the strategies and decisions that shaped the conflict. These leaders were not just figureheads; they were instrumental in directing military operations and influencing the course of the war.
British Leadership
British leadership during the Falklands War was characterized by strategic precision and decisive action. Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher was at the forefront, known for her firm resolve. She believed in defending British territory and was unwavering in her commitment, which rallied national support.
Admiral Sir John Fieldhouse, the Commander-in-Chief of the Task Force, was responsible for the operational planning. His naval background and strategic acumen were crucial. He ensured that the British forces maintained a tactical advantage in the South Atlantic.
The leadership extended to the ground with figures like Major General Jeremy Moore. He led the land forces with a clear focus on swift and effective military action. His leadership was vital in the successful recapture of the islands.
Argentinian Leadership
On the Argentine side, leadership was marked by a mix of ambition and miscalculation. The ruling military junta, led by General Leopoldo Galtieri, saw the invasion as a means to bolster national pride. However, the decision underestimated British resolve and international reaction.
Admiral Jorge Anaya was a key figure advocating for the military action. His influence within the junta pushed for a more aggressive stance. Yet, the lack of a comprehensive plan led to strategic shortcomings.
Brigadier General Mario Menéndez was appointed as the military governor of the Falklands. His command faced challenges due to logistical issues and morale problems. His leadership was tested by the harsh conditions and the tenacity of the British forces.
Reflecting on these leaders, one might consider how individual decisions in leadership can impact the broader trajectory of conflicts. How might different strategies have changed the outcome? Understanding these dynamics offers lessons in leadership and decision-making that are relevant even today.
Military Strategies
The Falklands War, fought in 1982, showcased strategic military maneuvers. Both Argentina and the UK employed complex tactics. Their strategies defined the course of the conflict. Exploring these strategies reveals key insights into naval and air operations.
Naval Operations
Naval forces played a crucial role in the Falklands War. The British Navy executed a maritime exclusion zone. This limited Argentine naval movements. They used aircraft carriers as floating airbases. This extended their reach across the South Atlantic. Destroyers and frigates provided escort and defense. Submarines patrolled the waters, hunting enemy vessels. The sinking of the Argentine cruiser, General Belgrano, was a turning point. This naval strike emphasized the importance of strategic naval power.
Air Combat Tactics
Air superiority was vital in the Falklands War. The British employed Harrier jets from carriers. These jets were versatile and agile in combat. They engaged Argentine aircraft in dogfights. Radar and intelligence were key for targeting accuracy. The British used Sea Harriers for air defense. Their vertical take-off capability provided flexibility. Argentine pilots relied on Mirage and Skyhawk fighters. They executed daring low-altitude attacks. Both sides faced challenges with weather and distance. Air tactics were crucial in the isolated Falkland skies.

Credit: www.iwm.org.uk
Turning Points In Battle
The Falklands War was a complex conflict. It involved tactical maneuvers and strategic decisions. These factors significantly influenced the outcome. Understanding the turning points in battle is crucial. It helps grasp how the war reached its conclusion. This section explores major engagements and influential decisions. These elements shaped the course of the war.
Major Engagements
The Battle of Goose Green stands out. It was one of the first major land battles. British forces faced strong resistance from Argentine troops. Despite challenges, British forces advanced. This victory boosted morale and confidence.
The naval engagement at the sinking of the Belgrano was significant. It marked a shift in naval strategy. British forces gained naval superiority. This allowed them to control key sea routes.
The Battle of Mount Tumbledown was crucial. British forces aimed to capture positions near Stanley. The fierce combat tested their resolve. Success here paved the way for the final advance.
Influential Decisions
The decision to deploy the Task Force was critical. It demonstrated Britain’s commitment to reclaiming the islands. This move showed determination to resolve the conflict.
The choice to use air superiority was strategic. British forces prioritized air attacks. This weakened Argentine defenses. It ensured control over crucial areas.
The decision to target Argentine supply lines was effective. It disrupted logistics and weakened enemy positions. British forces gained a tactical advantage.
The choice of night assaults played a vital role. These attacks surprised Argentine forces. They increased pressure and hastened the end of the conflict.
Diplomatic Efforts
Diplomatic efforts during the Falklands War sought peaceful solutions to the conflict. Talks between Britain and Argentina aimed at ending hostilities. Despite these attempts, tensions escalated, leading to military engagement.
The Falklands War, a ten-week conflict between Argentina and the United Kingdom in 1982, was not just a military showdown. It also involved significant diplomatic efforts. These efforts aimed to find a peaceful resolution to the conflict, which was rooted in both countries’ claims over the Falkland Islands. Despite the intensity of the situation, diplomatic channels were bustling with activity, striving to prevent further escalation.
Peace Negotiations
The diplomatic dance during the Falklands War included attempts at peace negotiations. The United Nations got involved, urging both nations to lay down arms. They pushed for a diplomatic solution, emphasizing dialogue over conflict.
Even though initial efforts did not yield results, they were crucial in setting a framework for future discussions. It was a race against time to find common ground. Imagine the pressure on diplomats, knowing lives depended on their decisions.
Have you ever faced a situation where finding middle ground seemed impossible? That’s what these negotiators dealt with daily. Despite setbacks, their persistence laid groundwork for eventual peace talks.
International Reactions
The world watched as the conflict unfolded, and international reactions varied. Some countries openly supported the UK, aligning with its sovereignty claims. Others backed Argentina, highlighting historical ties and regional solidarity.
Global organizations also chimed in, voicing concerns over regional stability. This was not just a two-nation issue; it had global implications.
How do you think these international reactions influenced the course of the war? They certainly added layers to an already complex situation. The diplomatic efforts were not just about direct negotiations; they involved managing these global perceptions too.
The Falklands War serves as a reminder of how critical diplomatic efforts are in conflict resolution. They may not always succeed immediately, but they set the stage for peace. Would you say the same about conflicts today? How much weight do you think diplomacy carries in our modern world?
Media Coverage And Public Opinion
The Falklands War in 1982 attracted global media attention. Reports and broadcasts shaped views worldwide. The media played a crucial role in influencing public opinion. This section explores the press influence and public sentiment during the conflict.
Press Influence
Media outlets provided extensive coverage of the Falklands War. Newspapers, radio, and TV channels reported daily updates. Journalists on the ground offered firsthand accounts. Their stories shaped perceptions of the conflict. British media often portrayed the war in patriotic terms. Argentine media emphasized national pride. Both sides sought to rally public support through the press. The media’s portrayal influenced international understanding of the war.
Public Sentiment
Public opinion varied in response to the media coverage. In Britain, many supported the war effort. The media’s portrayal of British troops as heroes fueled this support. In Argentina, the public showed strong nationalistic feelings. Media reports highlighted Argentina’s claims to the islands. Global audiences watched closely, forming their own opinions. The media’s influence on public sentiment was undeniable. It played a key role in shaping the narrative of the Falklands War.
Impact On Falkland Islanders
The Falklands War deeply affected the islanders’ daily lives. Many faced disruptions and fear during the conflict. The war’s aftermath brought lasting changes to their community and economy.
The Falklands War left an indelible mark on the lives of the islanders. The conflict, while short-lived, had lasting effects on the civilian population. Many were caught in the crossfire, and their lives were changed forever. Understanding their experiences can offer valuable insights into resilience and adaptation in the face of adversity.
Civilian Experiences
During the war, the everyday lives of Falkland Islanders were disrupted. Families found themselves caught in the midst of a military conflict that they did not anticipate. Imagine waking up to the sound of gunfire, unsure of what the day would bring.
Children’s schooling was interrupted as buildings were repurposed for military use. Many families had to take shelter, often in cramped and uncomfortable conditions. One islander recounted how they huddled in their home’s basement, listening to the distant sounds of battle and praying for safety.
The fear and uncertainty took a toll on mental health. Islanders had to grapple with the trauma of living in a war zone. How would you cope if your peaceful home turned into a battlefield overnight?
Post-war Changes
After the war, the Falkland Islands underwent significant transformation. The British government increased its military presence to ensure security. This brought economic benefits, but also changed the island’s dynamics.
Infrastructure development became a priority, improving roads and communication. This opened up new opportunities for trade and tourism, providing a boost to the local economy. For many islanders, these changes were a double-edged sword, offering both growth and the challenge of maintaining their cultural identity.
Education and healthcare saw improvements, providing a better quality of life. However, the memories of the war lingered, shaping how the islanders viewed their place in the world. How do you balance the benefits of progress with the desire to preserve your heritage?
The experience of the Falkland Islanders during and after the war offers a powerful lesson in resilience. It prompts us to reflect on how communities can adapt and thrive despite facing significant challenges.
Legacy And Consequences
The Falklands War left a significant mark on history. Its legacy and consequences continue to influence global politics and military strategies. This conflict, though brief, reshaped relationships and taught critical lessons. Understanding its aftermath offers insights into international diplomacy and defense strategies today.
Political Aftermath
The Falklands War reshaped British and Argentine politics. For Britain, victory boosted national pride. It strengthened Margaret Thatcher’s leadership. The war reinforced Britain’s commitment to protecting its territories. In Argentina, the defeat led to political turmoil. It sparked protests and weakened the ruling military junta. The war paved the way for Argentina’s return to democracy. Relations between the two nations remain tense. Territorial claims continue to stir diplomatic discussions.
Military Lessons
The Falklands conflict taught valuable military lessons. It highlighted the importance of air superiority. British forces relied heavily on effective air control. The war also showcased the significance of logistics and supply chains. Ensuring timely support proved crucial for operations. Naval power emerged as a decisive factor. The conflict underscored the need for advanced technology in warfare. Many countries reevaluated their military strategies post-war. Modern military doctrines still reflect these lessons.
FAQs
Why Did The UK Start The Falklands War?
The UK started the Falklands War to reclaim sovereignty over the Falkland Islands after Argentina’s invasion in 1982. The British government aimed to protect British citizens and assert their territorial rights, leading to a military conflict to regain control over the islands.
Who Won The Falklands War And Why?
The United Kingdom won the Falklands War in 1982. British forces reclaimed the islands from Argentine control. The conflict ended after 74 days, reinforcing British sovereignty over the Falklands. Military superiority and strategic planning contributed to the UK’s victory. The islands remain a British Overseas Territory today.
Did America Get Involved In The Falklands War?
America did not directly participate in the Falklands War. The United States provided intelligence and logistical support to Britain. While the U. S. aimed to maintain neutrality, it leaned towards supporting its ally, the United Kingdom, during the conflict between Argentina and Britain in 1982.
Why Did Argentina Start The Falklands War?
Argentina started the Falklands War to reclaim sovereignty over the islands. The military junta aimed to boost national pride and distract from domestic issues. The conflict with the United Kingdom erupted in 1982, rooted in a long-standing territorial dispute.
Conclusion
The Falklands War left a lasting impact on history. It reshaped global perceptions and military strategies. Both sides experienced significant losses, but gained important lessons. The conflict highlighted the complexities of territorial disputes. Lives were changed forever. Memorials now honor those who served bravely.
Understanding this war helps us prevent future conflicts. It reminds us of the importance of dialogue and diplomacy. Knowledge of the past guides our future actions. By learning, we grow wiser and more compassionate. The Falklands War teaches us the true cost of conflict.
Let’s embrace peace for a better world.