British history is a tapestry woven with a huge number of social impacts, from the early days of Roman rule to the multicultural society of today. As each period unfurled, significant social improvements left permanent marks on British identity, forming its literature, arts, social standards, and indeed language. This article explores a few of the key social milestones that have defined British history, outlining how each period contributed to the advancement of the nation’s rich social heritage.
The Roman Influence on Early British Culture
The Roman victory over Britain in 43 AD marked a noteworthy cultural turning point. The Romans presented urbanization, proven by towns like Londinium (modern-day London), as well as advanced architecture such as streets, baths, and villas. Latin became the dialect of administration, impacting the advancement of Ancient English. Perhaps most vitally, the Romans brought Christianity, planting the seeds for Britain’s devout identity, which would advance over the coming centuries.
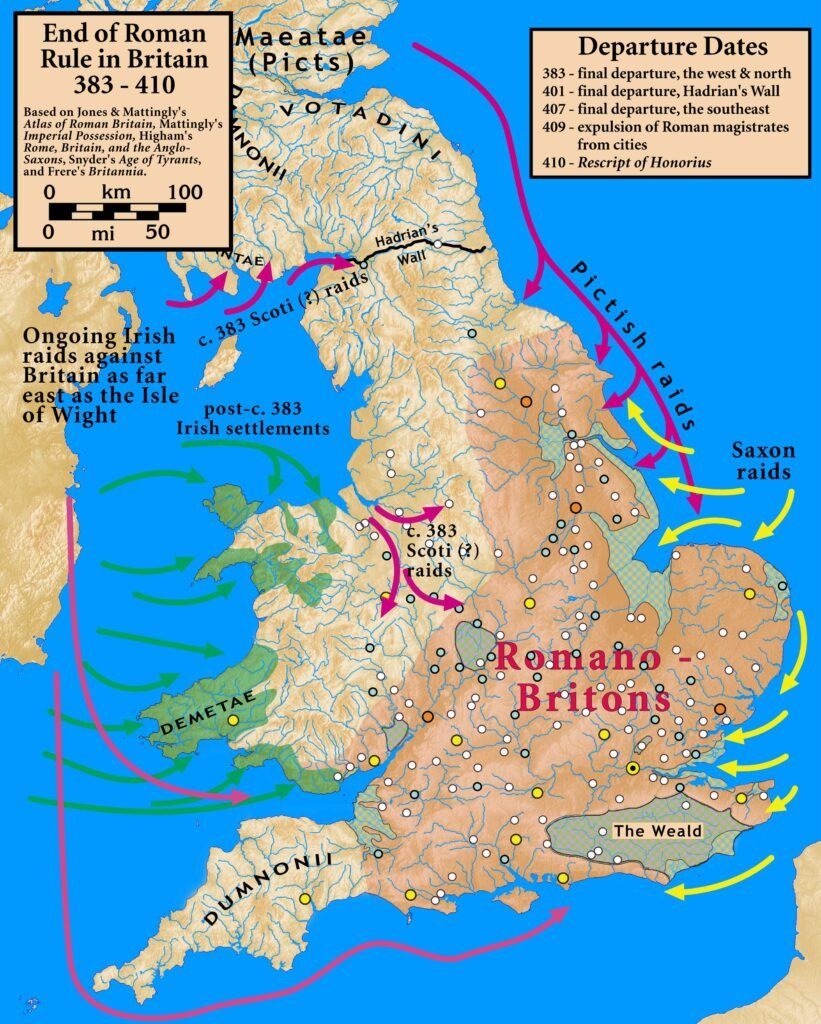
Anglo-Saxon and Viking Era
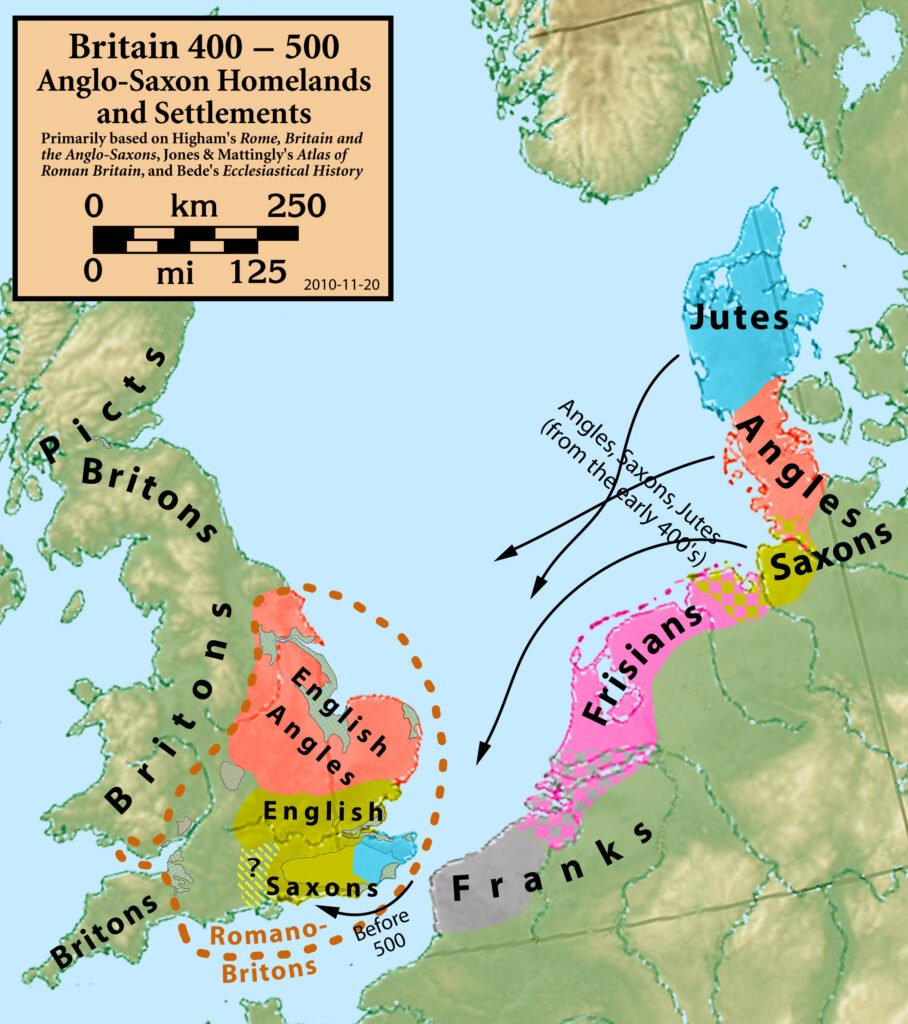
Following the Roman withdrawal, the Anglo-Saxons established themselves, laying the groundwork for English language and culture. The period saw the emergence of early English literature, with the epic poem Beowulf standing as a cornerstone. The Viking invasions also contributed to cultural exchange, seen in place names, language, and art. The blending of these cultures set the stage for the medieval period and the formation of the English nation.
The Norman Conquest and Medieval Britain
The Norman Victory in 1066 brought exceptional cultural changes. The Normans presented feudalism, rebuilt the social order, and left an enduring impact on the English language, infusing it with French vocabulary. The Gothic architectural style prospered during this time, epitomized by the construction of amazing cathedrals and castles. Also, the spread of chivalric standards and courtly literature reshaped societal values, impacting everything from poetry to legal systems.
The Renaissance and the Tudor Era
The Renaissance era breathed new life into British culture, especially during the Tudor reign. With figures like William Shakespeare and Christopher Marlowe at the forefront, English literature experienced a golden age. Simultaneously, the establishment of the Church of England under Henry VIII redefined religious and political life. The period also saw advancements in science and exploration, further enriching British intellectual and cultural pursuits.
The Enlightenment and the Age of Reason
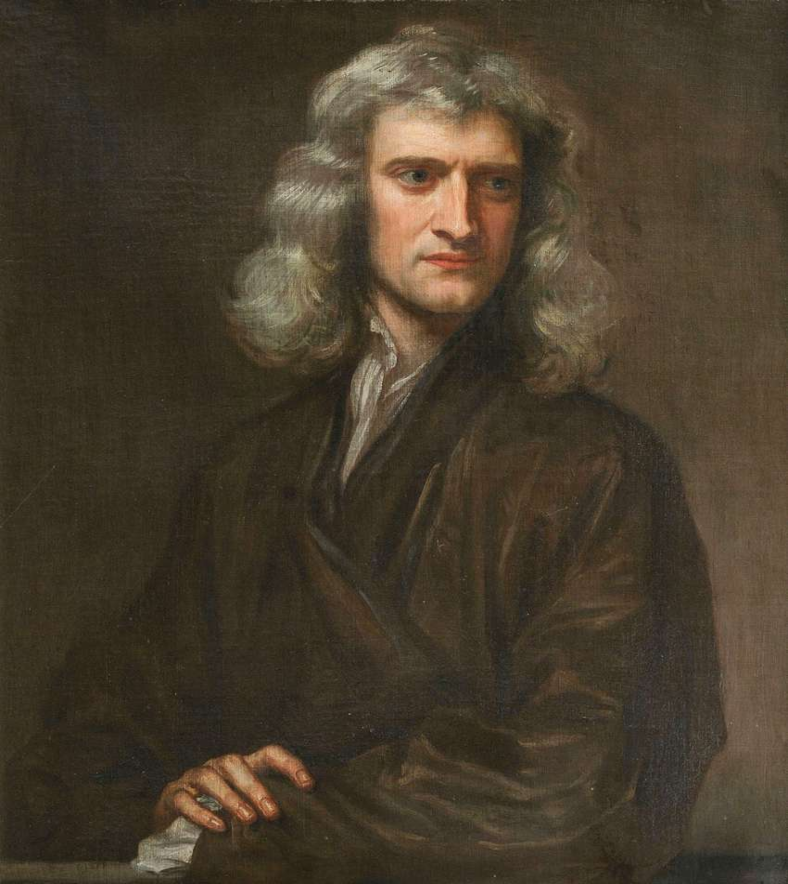
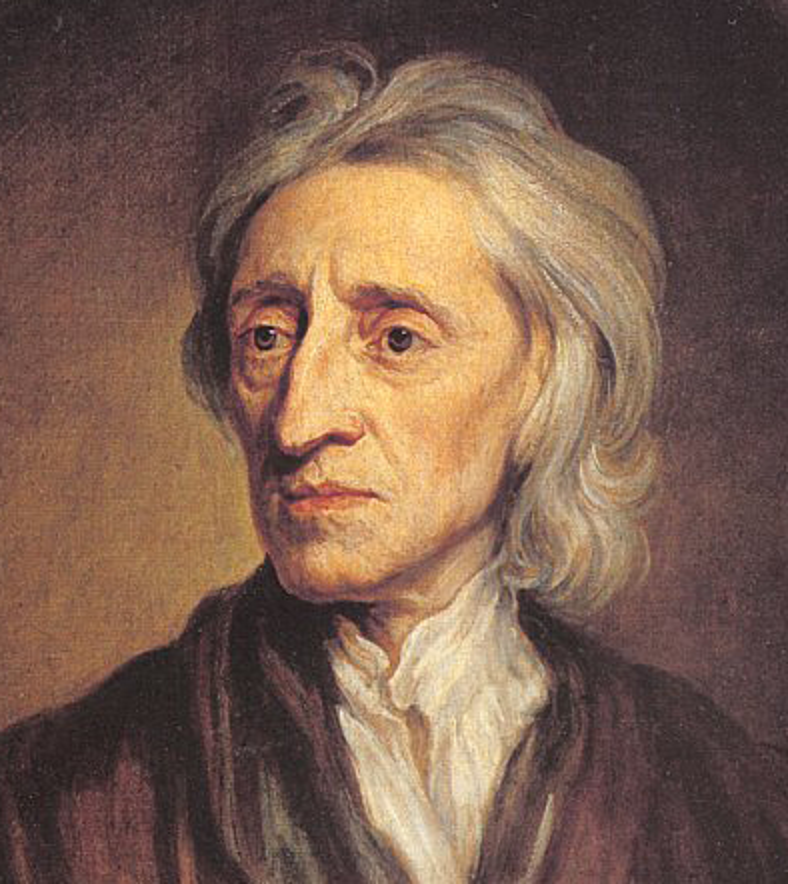
The Enlightenment brought about a surge in intelligence, with Britain rising as a center for scientific and philosophical thought. Masterminds like Isaac Newton revolutionized science, while John Locke’s compositions laid the establishment for modern democracy. The proliferation of books, pamphlets, and newspapers during this period democratized information, allowing ideas to spread broadly and influencing everything from politics to personal belief systems.


The Industrial Revolution and Social Change
The Industrial Transformation, starting in the late 18th century, changed British society. Urbanization, technological advancement, and the rise of factories moved the cultural landscape. The period also motivated literary giants like Charles Dickens, whose works strikingly depicted the challenges of industrial life. Meanwhile, the Romantic poets, including William Wordsworth and Lord Byron, reacted to these changes by celebrating nature and personal feelings, making a cultural counterbalance to industrialization.
Victorian Era: Morality, Empire, and Culture
The Victorian time was characterized by its strict ethical codes, the extension of the British Domain, and a flourishing cultural scene. The empire’s vast reach introduced new thoughts, goods, and cultural practices, making a sense of British superiority and global impact. In literature, authors like the Brontë sisters and Charles Dickens created immortal works that critiqued social issues. Furthermore, the era’s emphasis on family values and behavior left an enduring impact on British culture.
World War I and the Interwar Period
The consequence of World War I brought about significant cultural shifts. The horrors of the war led to a sense of frustration, reflected in the rise of modernist literature and art. Authors like Virginia Woolf and T.S. Eliot broke with conventional shapes, exploring topics of fragmentation and alienation. The interwar period moreover saw the emergence of the “Lost Generation,” whose works captured the lingering trauma and questioned pre-war societal standards.

Post-World War II Britain and the Welfare State
The post-World War II period marked the decay of the British Domain and the rise of the welfare state. Social reforms changed the lives of numerous Britons, while the conclusion of colonialism brought new cultural impacts from previous colonies. Well-known culture also prospered, with British music, especially The Beatles, leading a worldwide cultural revolution. The period also saw the advent of television as a dominant cultural constrain, reshaping amusement and communication.
The Swinging Sixties and Counterculture
The 1960s brought an outstanding move in British culture. The “Swinging Sixties” were characterized by an impact of creative ability in music, design, and craftsmanship. Bands such as the Beatles and The Rolling Stones not only revolutionized music but also formed global youth culture. The decade also saw a breakdown of conventional social standards, with the rise of counterculture challenging conservative values and advancing new thoughts of freedom and self-expression.
Thatcherism and the 1980s: Political and Cultural Shifts
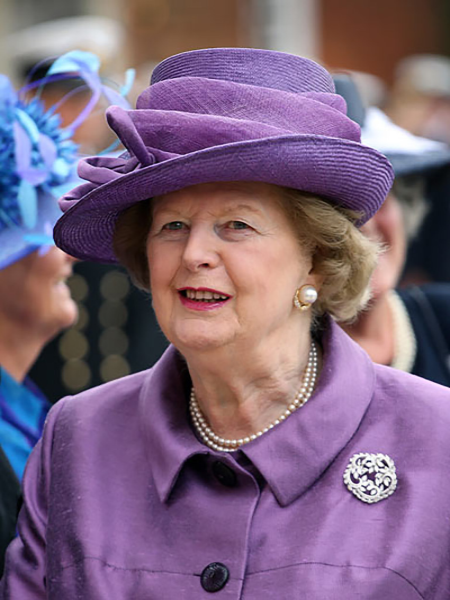

The 1980s were marked by noteworthy cultural changes under Margaret Thatcher’s authority. Her approaches of deregulation and privatization impacted everything from social structure to dominant culture. The decade saw the rise of punk rock as a form of rebellion against the foundation. British cinema and television moreover gained prominence, with gritty dramas and comedies that reflected the social realities of the time, contributing to the advancing British identity.
Multiculturalism and Modern British Identity
In later decades, British culture has been molded by the contributions of different communities. Immigration from former colonies and other parts of the world has enriched British society, impacting everything from food to fashion. The combination of diverse societies has made a dynamic and diverse society, though debates around national identity and integration stay continuous. Today, British culture is celebrated for its inclusivity and global viewpoint.
The Digital Age and Contemporary British Culture
The digital age has changed how culture is made and consumed. The internet and social media have given rise to new forms of expression, while the British inventive industries, including film, literature, and music, continue to flourish on the worldwide stage. British pop culture remains powerful around the world, from blockbuster movies like James Bond to music celebrations like Glastonbury. This modern period reflects Britain’s capacity to adapt and enhance while staying established in its wealthy cultural conventions.
Conclusion
All through history, Britain has been a softening pot of cultural impacts, each period leaving a distinct legacy. From Roman roads to Renaissance dramatization, and from Victorian morality to the advanced age, these cultural points of reference have collectively molded the nation’s identity. British culture is a dynamic blend of convention and innovation, reflecting both its chronicled roots and its openness to new thoughts.
FAQs
1. What were the main cultural impacts of the Norman Conquest?
The Norman Conquest introduced feudalism, Gothic architecture, and significant French influence on the English language.
2. How did the Industrial Revolution change British culture?
The Industrial Revolution led to urbanization, technological advancements, and inspired literary movements like Romanticism and social realism.
3. What role did the British Empire play in shaping British culture?
The British Empire introduced global influences to British society, shaping everything from cuisine to literature and contributing to a sense of British superiority.
4. How has immigration influenced modern British culture?
Immigration has enriched British culture with diverse cuisines, music, fashion, and has played a key role in shaping contemporary British identity.
5. What are some key examples of British contributions to global pop culture?
British music (The Beatles), literature (Shakespeare), and film (James Bond) have all had a lasting global influence, showcasing Britain’s cultural impact.








