The steam engine changed the world. It powered the Industrial Revolution.
In the 18th century, a remarkable invention transformed industries and transport. The steam engine, using steam to create mechanical motion, became a symbol of innovation. It allowed factories to move from water power to more flexible locations. Trains and ships, powered by steam, could transport goods and people faster than ever before.
This invention not only boosted production but also connected distant places. Understanding the steam engine’s impact helps us appreciate how technology can shape society. Let’s explore the fascinating history and significance of the steam engine.

Credit: www.livescience.com
Origins Of The Steam Engine
The steam engine represents a pivotal moment in human history. It powered the Industrial Revolution, transforming economies and societies. But how did it all begin?
Early Innovations
Early versions of steam engines date back to ancient Greece. Hero of Alexandria created the Aeolipile, a simple steam-powered device. It was not used for practical purposes. It was more of a curiosity. Over the centuries, inventors experimented with steam power. Progress was slow but steady.
In the 17th century, significant advancements took place. Inventors explored how steam could perform useful work. These early machines were inefficient. They were prototypes for the more advanced engines that followed.
Key Inventors
Thomas Savery was a key figure. In 1698, he patented a machine to pump water from mines. His engine used steam to create a vacuum. This device was not very efficient. It marked an important step forward.
Thomas Newcomen improved on Savery’s design. He created the atmospheric engine in 1712. It was used to pump water from mines. Newcomen’s engine was more practical. It became widely used.
James Watt took Newcomen’s design further. In 1765, Watt made a breakthrough. He added a separate condenser. This made the engine much more efficient. Watt’s steam engine powered factories, trains, and ships. It revolutionized industry.
These inventors laid the foundation for modern steam engines. Their work transformed the world. Each step built on the previous one. The steam engine’s origins are a story of innovation and progress.
How Steam Engines Work
The steam engine is a marvel of engineering. It has powered the industrial revolution and transformed our world. But how do steam engines work? Let’s dive into the basics and understand their operation.
Basic Principles
Steam engines operate on the principles of thermodynamics. Water is heated in a boiler until it turns into steam. The steam then expands and pushes against a piston or turbine. This movement creates mechanical energy.
The process begins with heating water. As the water boils, it turns into steam. The steam builds up pressure inside the boiler. This pressure is then used to do work. The cycle continues as the steam cools and condenses back into water.
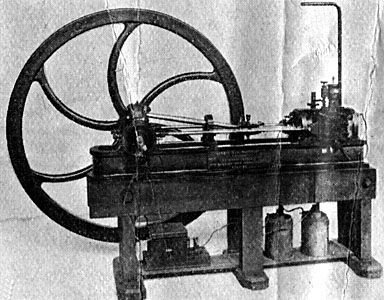
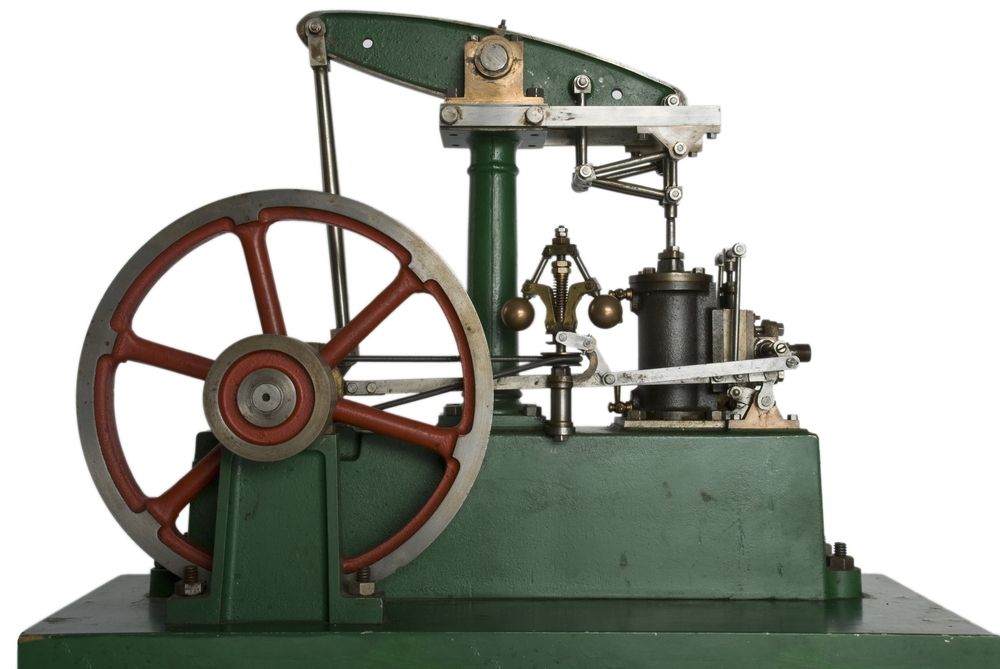
Key Components
A steam engine consists of several key components. Each plays a vital role in its operation.
Boiler: This is where water is heated and turned into steam. It must withstand high pressure and temperature.
Piston: The piston moves back and forth inside a cylinder. The steam pushes the piston, creating mechanical energy.
Valve: The valve controls the flow of steam into and out of the cylinder. It ensures the steam enters at the right time and exits after doing its work.
Condenser: The condenser cools the steam and turns it back into water. This water is then reused in the boiler.
Flywheel: The flywheel helps maintain a steady motion. It stores energy from the piston and releases it smoothly.
Understanding these components helps us appreciate the steam engine’s design. Each part works together to convert steam into mechanical energy efficiently.
Impact On Industry
The steam engine had a profound impact on various industries. It changed how goods were manufactured and transported. This innovation led to significant developments in industry and commerce. Below, we explore how the steam engine influenced manufacturing advancements and increased productivity.
Manufacturing Advancements
The steam engine introduced new possibilities in manufacturing. Factories no longer relied on water or wind power. This meant factories could be built anywhere, not just near rivers or windy places. The flexibility allowed industries to grow in urban areas.
With the steam engine, machines operated more efficiently. Factories could produce goods faster. This led to the creation of new products and industries. The textile industry, in particular, saw huge growth. Steam-powered machines replaced manual labor, boosting production.
| Advancement | Impact |
|---|---|
| Location Flexibility | Factories built in urban areas |
| Efficiency | Machines operated faster and better |
| Production | Increased output in textile and other industries |
Increased Productivity
The steam engine drastically increased productivity. Machines could run continuously without tiring. This led to longer working hours and more goods produced. Industries could meet the growing demand of a booming population.
Steam engines also improved transportation. Trains and ships powered by steam moved goods quickly and efficiently. This meant raw materials could reach factories faster. Finished products were distributed widely, boosting trade and commerce.
- Continuous machine operation
- Longer working hours
- Quick transportation of raw materials
- Efficient distribution of finished products
Overall, the steam engine marked a pivotal shift. It transformed industries and paved the way for modern manufacturing and transport.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Revolutionizing Transportation
The steam engine transformed transportation. It made travel faster and more efficient. This innovation reshaped how people and goods moved across the world. The impact was profound and long-lasting.
Railway Expansion
Railways expanded rapidly with the steam engine. Trains could travel long distances quickly. This connected cities and towns like never before. Goods reached markets faster. Travel became more accessible for people. The economy grew as a result. The steam locomotive was at the heart of this change.
Steamships
Steamships changed sea travel. They were faster than sailing ships. Steamships could travel against the wind. This made sea routes more reliable. Trade between continents flourished. Steamships carried people across oceans. They made global travel a reality. The steam engine powered this maritime revolution.
Economic Effects
The steam engine was a major innovation in human history. Its impact on the economy was enormous. It transformed industries and changed lives. Let’s explore its economic effects in detail.
Trade Growth
The steam engine boosted trade significantly. Ships powered by steam could travel faster. They carried more goods, reaching distant markets with ease. This expansion of trade opened new opportunities. Businesses grew and new markets emerged. The steam engine made the world more connected. It played a key role in global trade.
Job Creation
The rise of the steam engine led to many new jobs. Factories needed workers to operate steam-powered machines. Railways required labor for construction and maintenance. New industries emerged, creating more employment opportunities. People moved from rural areas to cities. They sought better-paying jobs in these growing industries. This shift contributed to urbanization and economic growth.
Social Implications
The steam engine brought significant social implications. Its impact went beyond technology. It altered daily life and societal structures. This section delves into those changes.
Urbanization
The steam engine fueled urbanization. People moved to cities for work. Factories sprang up, needing workers. Cities grew rapidly. Life in cities changed. Streets buzzed with activity. New neighborhoods developed. Infrastructure expanded. The steam engine changed the landscape. It shaped modern cities.
Changing Workforce
The steam engine changed the workforce. Skilled labor was in demand. Factories required operators and engineers. Women and children joined the workforce. Working hours increased. The nature of work shifted. Handcraft jobs declined. Factory jobs rose. New opportunities emerged. The workforce evolved.
Technological Advancements
The steam engine has been a cornerstone of technological progress. It has transformed industries and powered various machines. Over the years, several advancements have improved its efficiency and expanded its uses.
Improved Efficiency
Early steam engines were not very efficient. They wasted a lot of energy. But, over time, engineers made significant improvements.
- James Watt’s separate condenser: Reduced heat loss and saved fuel.
- High-pressure steam: Increased power output without adding much size.
- Double-acting cylinders: Allowed steam to push on both sides of the piston.
These innovations made steam engines more reliable and powerful. They could now do more work with less fuel.
Innovative Uses
As steam engines became more efficient, their applications widened. They were no longer limited to pumping water from mines.
Some innovative uses include:
- Transportation: Steam engines powered trains and ships, making travel faster.
- Manufacturing: Factories used steam engines to run machines, increasing production.
- Agriculture: Steam tractors helped in plowing fields and harvesting crops.
These uses revolutionized various sectors. They paved the way for the Industrial Revolution.
Today, steam engines are mostly historical. Yet, their impact on technology remains significant. The principles learned from them still apply in modern engines.
Legacy Of The Steam Engine
The legacy of the steam engine is profound. It transformed industries, societies, and economies. The steam engine was a catalyst for the Industrial Revolution. Its impact is still felt today, in both historical context and modern applications.
Modern Applications
Steam engines are not just relics of the past. They have modern uses. Many power plants still use steam engines for electricity generation. Steam turbines convert steam into mechanical energy. This process powers generators.
In the medical field, steam is used for sterilization. Autoclaves use steam to kill bacteria and viruses. This ensures medical tools are safe for use.
Steam engines also play a role in education. Many museums showcase working models. These models educate people about engineering and history.
Historical Significance
The steam engine had a major impact on history. It powered the first industrial machines. Factories could produce goods faster and cheaper. This led to mass production and urbanization.
Steam engines also transformed transportation. Trains and steamships could travel long distances. This made trade and travel easier. The world became more connected.
Here are some key points about the historical significance of the steam engine:
- Increased production efficiency
- Enhanced transportation capabilities
- Facilitated global trade and communication
- Spurred economic growth and urban development
The steam engine’s legacy is vast. It changed how we live and work. Its impact on history and modern life is undeniable.
FAQs
What Is A Steam Engine?
A steam engine is a machine that converts steam energy into mechanical work. It’s an early form of power generation.
Who Invented The Steam Engine?
The steam engine was invented by Thomas Newcomen in 1712. Later, James Watt made significant improvements in the 1760s.
How Does A Steam Engine Work?
A steam engine works by heating water to produce steam. The steam then drives a piston or turbine to generate power.
What Are The Uses Of Steam Engines?
Steam engines were used in various industries, including railways, factories, and ships. They powered machinery and transportation.
Conclusion
The steam engine changed the world. It powered industries and transformed transport. Its invention marked a new era in human history. Today, we see its impact everywhere. From factories to trains, its legacy lives on. Understanding its history helps us appreciate modern technology.
The steam engine was the start of something great. It laid the foundation for today’s advancements. Let’s remember its importance and continue innovating. The steam engine’s story is one of progress. It reminds us of human ingenuity and the drive to improve.